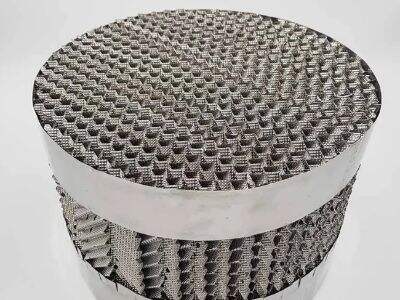
Two general categories of packing used in industries are known as structured packing and random packing. How they are different from each other? Let’s find out!
What is Structured Packing?
It is like a neat puzzle, Structured packing. It has created organized rows and columns in materials that provide large surface areas for liquids and gases to mix. This allows separation and transfer of various substances.
What is Random Packing?
Random packing is more of a slobbery pile. It is just a few materials in all different shapes shoved into a box. While blending may be the primary premise of the task, random packing may aid with scattering and thereby result in better mixing, which is helpful in some processes where mixing is critical.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Structured Packing
When it comes to applications that require high efficiency and precision, such as distillation and absorption, structured packing shines. This is good for separating stuff, and is common in high-quality critical and central industries.
Yet structured packing can cost significantly more and be more difficult to install than random packing. It also can get blocked if it doesn't get cleaned up and this can reduce efficiency over time.
Benefits of Random Packing
Random packing is better for applications where thorough mixing and movement of materials occurs, such as in wastewater treatment and air pollution control. Its messy arrangement encourages the creation of movement, leading to effective processes.
Structured packing is typically more expensive and harder to install than random packing. It is designed to address continuous operations, as it can process a large amount of flow without further losing efficiency.


 EN
EN
 ES
ES PT
PT SV
SV DE
DE TR
TR FR
FR